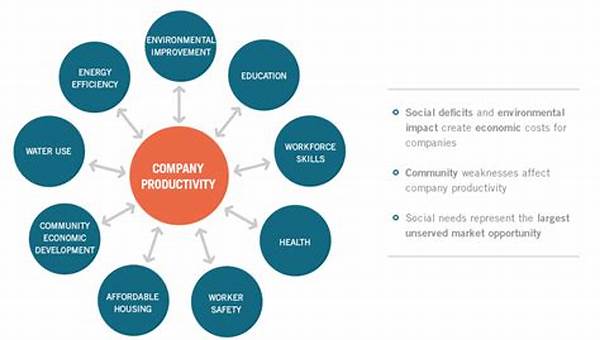
Understanding the Concept of Shared Value Creation in Innovation
Shared value creation in innovation represents a paradigm shift in both the corporate and societal landscapes. It postulates that businesses can generate economic value in a way that also produces value for society by addressing its challenges. This model transcends the traditional practice of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) by embedding social good into the core business strategy rather than treating it as a peripheral activity. Companies that adopt shared value creation in innovation aim not only to enhance their competitive advantage but also to propel societal progress through their operational activities.
Read Now : Effective Student-centered Learning Strategies
The impetus for shared value creation in innovation stems from the recognition that the well-being of communities and the environment is integral to long-term business success. As society faces challenges such as climate change, inequality, and resource scarcity, companies have the opportunity to innovate solutions that contribute positively to these issues while fostering business growth. This approach demands a reevaluation of how value is defined and understood within the corporate context, focusing on mutual benefits rather than zero-sum outcomes. By aligning business success with societal progress, shared value creation in innovation can lead to sustainable development that benefits multiple stakeholders.
In practice, shared value creation in innovation often involves devising new products or services that meet societal needs, reconfiguring value chains for greater social impact, or enabling local cluster development to benefit both the company and the community. These initiatives are not just philanthropic but strategic actions that harness a company’s unique resources and expertise. It is increasingly evident that businesses embracing shared value creation in innovation tend to enjoy stronger reputations, increased customer loyalty, and enhanced economic performance as they meet the contemporaneous demands of both consumers and society.
Key Benefits of Shared Value Creation in Innovation
1. Societal Advancement: Shared value creation in innovation drives societal progress by directly addressing social and environmental challenges. By integrating these concerns into business strategies, enterprises can play a pivotal role in solving pressing global issues.
2. Competitive Edge: Companies that pioneer shared value creation in innovation often achieve a competitive advantage. By offering unique solutions that distinguish them from their competitors, they can attract customers and partners who prioritize ethical and sustainable practices.
3. Sustainable Growth: Shared value creation in innovation encourages sustainable development. By focusing on long-term community welfare and environmental conservation, businesses can ensure their operations remain viable and profitable over time.
4. Enhanced Corporate Reputation: Companies engaging in shared value creation in innovation experience improved brand perception. By demonstrating a commitment to societal good, they build trust and credibility among consumers, investors, and the public.
5. Market Expansion: Focusing on shared value creation in innovation allows businesses to tap into new markets. By addressing underserved communities or unmet needs, they can stimulate demand and foster new revenue streams.
Strategic Implementation of Shared Value Creation in Innovation
Adopting shared value creation in innovation requires a strategic approach that aligns business objectives with societal goals. The initial step involves identifying intersections between social issues and corporate capabilities. Companies must map out how their resources, expertise, and market access can be leveraged to address societal challenges effectively. This necessitates a deep understanding of both business dynamics and social needs.
Once these intersections are identified, businesses should focus on designing new business models or enhancing existing ones that can simultaneously deliver societal and economic benefits. This could involve developing sustainable supply chains, launching products that meet social needs, or harnessing technology to minimize environmental impact. Throughout the process, companies must engage stakeholders, including communities, governments, and non-profits, to ensure their initiatives are viable and impactful. Implementing shared value creation in innovation is a dynamic, ongoing process wherein companies constantly refine their strategies in response to evolving societal contexts and business landscapes.
Challenges in Implementing Shared Value Creation in Innovation
1. Complexity in Alignment: Aligning business goals with societal needs can be complex, as each has its own set of priorities, constraints, and timelines.
2. Resource Allocation: The shift toward shared value creation in innovation may demand significant resources, including time, money, and expertise.
3. Stakeholder Engagement: Successfully implementing shared value creation in innovation necessitates active collaboration with diverse stakeholders, each with different expectations and influences.
4. Measuring Impact: Quantifying the benefits of shared value creation in innovation can be challenging, requiring robust frameworks to assess societal and business impacts.
5. Organizational Change: Embedding shared value creation in innovation necessitates cultural and organizational shifts that can face resistance within the company.
6. Market Dynamics: Rapid changes in market trends can affect the success of initiatives focused on shared value creation in innovation.
7. Regulatory Environment: Compliance with existing laws and regulations can influence the feasibility of shared value creation in innovation.
Read Now : “crafting A Focused Study Setting”
8. Risk Management: There are inherent risks in pursuing shared value creation in innovation, including potential failures of new business models or initiatives.
9. Technological Challenges: Leveraging technology for shared value creation in innovation might require significant investment in research and development.
10. Consumer Awareness: Educating consumers on the value of innovation-driven shared value can pose challenges, as awareness levels vary widely.
11. Competitive Pressure: Maintaining competitive advantage while pursuing shared value creation in innovation requires constant innovation and adaptation.
12. Long-Term Commitment: Shared value creation in innovation relies on maintaining long-term investments and commitments, which may conflict with short-term business targets.
Case Studies of Shared Value Creation in Innovation
Examining real-world examples of shared value creation in innovation can provide valuable insights and lessons for businesses seeking to adopt this approach. One notable case is a leading global food company that addressed malnutrition and health issues by developing nutrient-rich products tailored to the needs of low-income populations. By engaging local farmers, improving their livelihoods, and sourcing ingredients sustainably, the company not only expanded its market but also made a substantial positive impact on public health and economic development.
Another exemplary case is a technology firm that leveraged its expertise to reduce electronic waste through innovative recycling solutions. This initiative not only tackled a significant environmental issue but also created a circular economy model that offered new business opportunities and revenue streams. By fostering partnerships with governments and NGOs, the firm was able to scale its efforts, enhancing both its ecological footprint and market presence.
These examples illustrate the transformative potential of shared value creation in innovation in diverse industries. By viewing societal challenges as opportunities for growth and value creation, businesses can achieve a harmonious balance between profit and purpose. The success of these initiatives underscores the importance of strategic foresight, cross-sector collaboration, and a deep-seated commitment to sustainable development, all essential components of the shared value creation in innovation ethos.
Emerging Trends in Shared Value Creation in Innovation
In recent years, emerging trends in shared value creation in innovation have signaled a robust evolution in how businesses engage with their environments. One such trend is the increased alignment of corporate goals with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Many businesses now see aligning with these global objectives as a pathway to identify new opportunities for shared value creation in innovation. By aligning with SDGs, companies ensure their contributions drive positive social change and generate mutual benefits.
Another trend is the rise of technology-driven innovations aimed at solving social issues. The use of artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things has enabled businesses to create impactful solutions at a faster pace and larger scale. These technologies allow companies to devise creative ways of addressing social needs, thus illustrating the potency of shared value creation in innovation within the tech sector.
Furthermore, there has been a notable increase in collaborative ecosystems involving multiple stakeholders, including corporations, governments, non-profits, and academic institutions. These partnerships foster innovative thinking and amplify the impact of shared value creation endeavors. As businesses prioritize collaboration over competition, they can pool resources and expertise to tackle complex societal issues more effectively.
Overall, these trends demonstrate a promising future for shared value creation in innovation, as organizations continue to evolve and redefine the intersection of profitability and sustainability in today’s socio-economic landscape.
Conclusion: The Future of Shared Value Creation in Innovation
In summary, shared value creation in innovation represents a paradigm where business objectives and societal needs coalesce, fostering an environment where both can thrive symbiotically. As explored in various sections, this concept transcends traditional CSR, embedding societal consciousness directly into the core of business strategies. Companies that embrace this approach are better positioned to confront global challenges, tap into new markets, and achieve sustainable growth, ultimately leading to mutual benefits for both society and the enterprise itself.
As businesses continue to evolve alongside emerging trends and navigate the associated challenges, it is clear that shared value creation in innovation holds immense potential to reshape industries. By adopting strategic foresight, fostering cross-sector collaborations, and committing to sustainable practices, companies can not only drive economic success but also engender significant societal advancements. The future of shared value creation in innovation is poised to transform conventional business paradigms, promoting a world where innovation leads to inclusive and equitable prosperity.