The increasing reliance on digital platforms in modern enterprises necessitates robust security measures to protect sensitive information. As businesses transition to IT-based operations, the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data become paramount. Securing sensitive information systems is not merely a technical requirement but a critical component of corporate strategy, communication, and trust-building among stakeholders. As cyber threats evolve with technology, organizations must prioritize an integrated and comprehensive approach to information security. This process involves understanding the nuances of current threats, implementing vigilant monitoring, and deploying innovative solutions, all while fostering a security-centric culture.
Read Now : Cultivating Artistic Skills In Children
Understanding the Importance of Information Security
Information security, especially the aspect of securing sensitive information systems, serves as the backbone of modern enterprise infrastructure. This layer of protection ensures that sensitive data, comprising proprietary corporate information, customer details, and financial transactions, remains uncompromised. In recent years, breaches have caused significant financial and reputational damage to organizations worldwide. Therefore, it is imperative for companies to adopt effective security frameworks that encompass data encryption, access control, and regular audits. By embedding security protocols within the fabric of business processes, organizations can transform vulnerabilities into competitive advantage, reinforcing stakeholder confidence and complying with regulatory mandates.
Key Elements of Securing Sensitive Information Systems
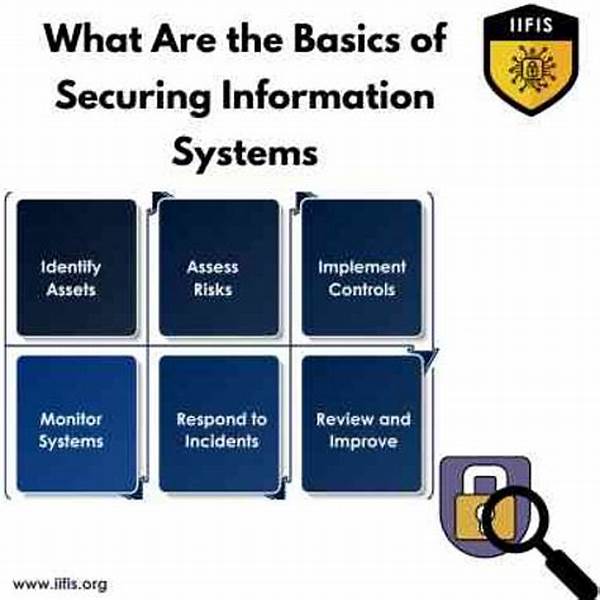
1. Access Control: Ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information is essential in securing information systems. Implementing robust identity verification and multi-factor authentication methods is critical to maintaining system integrity.
2. Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest is a fundamental step in securing information systems. It prevents unauthorized access and ensures the confidentiality of the data.
3. Regular Audits and Monitoring: Regular system audits and monitoring help identify potential vulnerabilities and address them promptly. Continuous assessment and improvement are vital for securing sensitive information systems.
4. Employee Training: Training employees on cybersecurity policies and potential threats creates a first line of defense against breaches. Awareness and education are critical components in securing sensitive information systems.
5. Incident Response Plan: Developing a comprehensive incident response plan ensures quick recovery and mitigation of impact in the event of a security breach. It is a crucial element in the strategy of securing sensitive information systems.
Building a Security-Conscious Culture
Creating an organizational culture that emphasizes the importance of securing sensitive information systems is as crucial as implementing technical measures. Employees, often considered the weakest link in security chains, need proper training and awareness programs. By fostering a culture where information security is a shared responsibility, businesses can significantly reduce their vulnerability. Leadership involvement is required to instill security principles into the core values and operational policies. Promoting best practices, rewarding vigilance, and integrating security discussions into routine meetings can reinforce the mindset required for effective information system security.
Read Now : Adaptable Education Delivery Approaches
Challenges in Securing Sensitive Information Systems
Securing sensitive information systems undoubtedly presents multiple challenges. First, the dynamic nature of cyber threats requires constant vigilance and adaptability. Organizations need to stay ahead of potential threats by investing in advanced threat detection and response technologies. Additionally, balancing security and usability is crucial; overly restrictive measures may hamper productivity and user experience, whereas leniency could expose systems to attacks. Furthermore, securing sensitive information systems requires substantial financial investment, which might be a constraint for smaller entities. These challenges demand a strategic approach, emphasizing not just technology but also policy, process, and people.
Best Practices for Information System Security
Standardizing best practices is essential for effectively securing sensitive information systems. Firstly, regular updates and patches are necessary to address vulnerabilities. Automated systems can assist in managing this efficiently. Secondly, employing advanced encryption standards for data protection must remain a priority. Thirdly, access controls should be revisited regularly to minimize risks associated with personnel changes. Additionally, engaging in routine penetration testing can identify potential weaknesses that need addressing. Together, these strategies build a robust framework for protecting sensitive information, which is central to maintaining corporate trust and credibility.
The Role of Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance plays a pivotal role in securing sensitive information systems. Frameworks such as the GDPR and HIPAA set benchmarks for data protection practices, ensuring that organizations follow legal protocols for data handling. Complying with these regulations is not merely about avoiding penalties but about setting a higher standard for data privacy and protection. Aligning with these regulations involves a thorough understanding of obligations and proactive measures to integrate required practices into daily operations. Organizations must continuously evaluate their compliance status to ensure adherence and adjust policies as necessary.
Conclusion
Securing sensitive information systems is an ongoing commitment that organizations must uphold to protect corporate and personal data. Implementing comprehensive security frameworks and fostering a culture of vigilance and resilience are essential steps toward safeguarding critical information. As threats become increasingly sophisticated, companies must adapt swiftly, leveraging technological advancements and regulatory guidelines to fortify their defenses. By prioritizing information security, businesses can not only safeguard their assets but also build enduring trust with their stakeholders, ensuring a secure digital footprint well into the future.