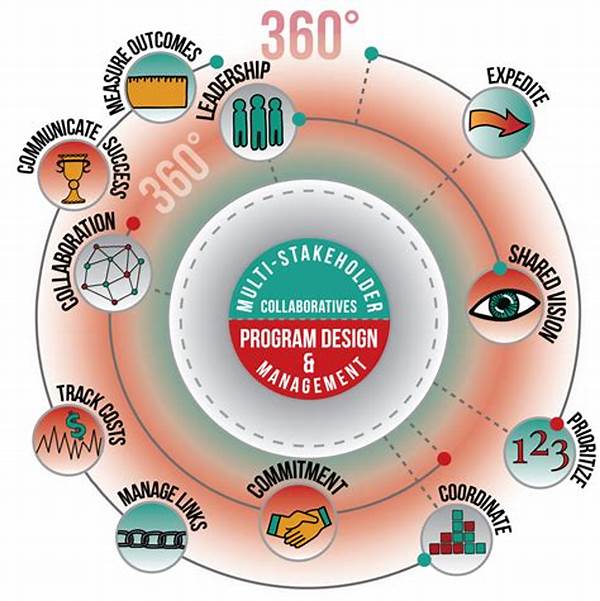
The Importance of Multi-Stakeholder Partnerships
In today’s interconnected world, multi-stakeholder partnership models have gained significant importance in addressing complex global challenges. These models emphasize collaboration among diverse actors, including governments, non-governmental organizations, and the private sector. By fostering an inclusive environment, these partnerships leverage each stakeholder’s strengths to create innovative solutions. The flexibility and adaptability inherent in multi-stakeholder partnership models ensure that they can respond effectively to ever-changing global dynamics. The growing trend towards globalization and interconnectedness has highlighted the necessity for cooperative approaches in tackling issues such as climate change, sustainable development, and public health, where single-entity attempts might not suffice.
Read Now : Hands-on Math Projects For Kids
Moreover, multi-stakeholder partnership models encourage transparency and accountability, critical elements for building trust among participants. By ensuring that each stakeholder’s voice is heard equally, these partnerships facilitate a balanced approach to problem-solving. This inclusivity enhances the legitimacy and acceptance of decisions made within the group, thereby leading to more sustainable and widely adopted outcomes. These collaborations often result in shared resources and knowledge, which can significantly enhance the effectiveness of the initiatives undertaken. In this manner, the synergies created by multi-stakeholder partnership models contribute to their success.
Finally, multi-stakeholder partnership models facilitate long-term engagement by creating platforms for continuous dialogue and interaction. This ongoing communication not only ensures that the initiatives remain relevant but also allows for the integration of new stakeholders and ideas over time. This dynamic nature of the partnerships enables them to adapt to evolving challenges and incorporate innovative solutions. Through structured collaboration, multi-stakeholder partnership models offer a pragmatic framework to address multifaceted issues that single entities may find overwhelming. The comprehensive approach promotes resilience, adaptability, and innovation, ensuring that these partnerships remain a preferred strategy to tackle the world’s pressing issues.
Characteristics of Effective Multi-Stakeholder Partnerships
1. Inclusivity: Effective multi-stakeholder partnership models prioritize inclusivity by engaging a diverse range of stakeholders who can bring various perspectives to the table. This inclusivity ensures that different viewpoints are considered, promoting holistic and balanced decision-making processes.
2. Transparency: Multi-stakeholder partnership models operate on a foundation of transparency, enabling all stakeholders to have clear insights into decision-making processes and outcomes. Transparency builds trust and fosters an environment where collaboration can thrive.
3. Accountability: In multi-stakeholder partnership models, accountability is crucial for maintaining trust among participants. Clearly defined roles and responsibilities ensure that all stakeholders are held accountable for their contributions and commitments, thereby enhancing the partnership’s credibility.
4. Flexibility: The dynamic nature of multi-stakeholder partnership models requires flexibility to adapt to evolving challenges and incorporate new insights. Flexibility allows partnerships to remain relevant and effective over time, addressing both current and future issues.
5. Shared Goals: Multi-stakeholder partnership models are united by shared goals and objectives, which align the efforts of different stakeholders and create a sense of collective purpose. This unity strengthens collaborative endeavors and drives partnerships toward achieving desired outcomes.
Challenges in Implementing Multi-Stakeholder Partnership Models
Implementing multi-stakeholder partnership models can present several challenges, despite their potential for positive outcomes. One significant challenge is the difficulty in aligning the interests and priorities of diverse stakeholders. Each participant may have differing objectives, which can lead to conflicts and hinder effective collaboration. Furthermore, balancing power dynamics among stakeholders is often a complex task, requiring careful negotiation and mediation to ensure equitable participation. These challenges necessitate strong leadership and facilitation skills to guide the partnership and maintain a focus on common goals.
Another critical issue is the resource disparity between stakeholders within multi-stakeholder partnership models. Some participants may have significant resources, both financial and human, while others may lack the necessary capacity to contribute effectively. This imbalance can create tensions and undermine the cooperative spirit of the partnership. Additionally, the multi-layered and complex nature of these partnerships can result in slow decision-making processes, as consensus must be reached across various parties. This can delay the implementation of essential initiatives and frustrate stakeholders who seek timely outcomes.
To overcome these challenges, it is essential to establish robust governance structures within multi-stakeholder partnership models. Clearly defined rules of engagement, regular communication, and transparent processes can facilitate smoother interactions and decision-making. By recognizing and addressing these obstacles proactively, stakeholders can maximize the potential of these partnerships to deliver innovative solutions to global challenges. An emphasis on continual improvement and adaptation is key to sustaining successful multi-stakeholder collaborations over time.
Strategies for Enhancing Multi-Stakeholder Partnerships
1. Developing Clear Communication Channels: Establishing effective communication channels is vital for the success of multi-stakeholder partnership models. Clear and consistent communication ensures that all stakeholders are informed, reducing misunderstandings and fostering coordinated action.
2. Building Trust Among Participants: Trust is the foundation of any successful collaboration. Multi-stakeholder partnership models should focus on building trust among participants through transparency, accountability, and respect for diverse perspectives.
3. Facilitating Continuous Learning: Multi-stakeholder partnership models benefit from a culture of continuous learning. Encouraging knowledge sharing and learning from past experiences enhances the partnership’s ability to innovate and adapt over time.
4. Ensuring Equal Power Dynamics: Equitable power dynamics are crucial in multi-stakeholder partnership models. Efforts should be made to balance influence among stakeholders, ensuring that all voices are heard and considered in decision-making processes.
Read Now : Realtor Ethics And Compliance Education
5. Promoting Flexibility and Adaptability: Multi-stakeholder partnership models must remain flexible to adapt to new challenges and opportunities. Encouraging adaptability allows partnerships to respond effectively to changing circumstances and emerging issues.
6. Establishing Shared Metrics for Success: Defining common metrics for evaluating success can align stakeholders’ efforts towards achieving shared goals. These metrics provide transparency and accountability, facilitating collaborative progress in multi-stakeholder partnership models.
7. Fostering a Cohesive Vision: Developing a cohesive vision that aligns stakeholders around a common purpose strengthens multi-stakeholder partnership models. This shared vision promotes cooperative efforts and fosters commitment to achieving collective objectives.
8. Leveraging Technological Solutions: Technological solutions can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of multi-stakeholder partnership models. Embracing digital tools for communication and collaboration enables more agile and dynamic partnerships.
9. Encouraging Stakeholder Engagement: Active engagement of stakeholders is essential for the vibrancy of multi-stakeholder partnership models. Facilitative processes should be in place to ensure high levels of participation and inclusivity.
10. Enhancing Conflict Resolution Mechanisms: Effective conflict resolution mechanisms are vital to address disputes among stakeholders in multi-stakeholder partnership models. These mechanisms enable partnerships to navigate disagreements and focus on common objectives without derailing progress.
11. Supporting Capacity Building Initiatives: Multi-stakeholder partnership models should prioritize capacity building to empower all stakeholders. Providing training and resources enhances each participant’s ability to contribute effectively to the partnership.
12. Maintaining Long-term Commitment: Sustained effort and commitment are essential for the longevity of multi-stakeholder partnership models. Long-term engagement allows partnerships to evolve and remain impactful over time, addressing ongoing and emerging challenges.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Multi-Stakeholder Partnerships
Evaluating the effectiveness of multi-stakeholder partnership models requires a comprehensive approach that considers both qualitative and quantitative factors. Metrics such as stakeholder satisfaction, goal alignment, and outcome achievement are critical indicators of success. Regular assessments can provide insights into areas of improvement and avenues for enhancing collaboration. Importantly, the evaluation process should be participatory, involving feedback from all stakeholders to ensure that the assessment is balanced and accurately reflects the partnership’s impact. This participatory approach not only reinforces transparency but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
Furthermore, effective evaluation of multi-stakeholder partnership models involves analyzing the adaptability and resilience of the partnerships. The ability to respond to evolving challenges and incorporate innovative solutions is a testament to a partnership’s robustness. Flexibility in operations and decision-making processes often reflects the partnership’s capacity to navigate complex global issues. These evaluations should be iterative, allowing for adjustments and course corrections that can enhance the partnership’s ability to achieve its objectives. Ultimately, robust evaluation frameworks contribute to the sustainability and success of multi-stakeholder partnerships, enabling them to remain effective in the face of ongoing and emerging challenges.
Conclusion: Embracing Multi-Stakeholder Partnership Models
In conclusion, multi-stakeholder partnership models represent a strategic approach to tackling complex global challenges by leveraging the collective strengths and resources of diverse actors. Through inclusivity, transparency, and accountability, these partnerships provide a framework for effective collaboration among governments, non-governmental organizations, and the private sector. Despite the challenges inherent in aligning varied interests and addressing resource disparities, the benefits of multi-stakeholder partnership models far outweigh the limitations. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptability, these partnerships can adapt to evolving global dynamics and remain resilient in the face of new challenges.
Moving forward, the continued success of multi-stakeholder partnership models will depend on enhanced communication, trust-building, and shared vision among stakeholders. As these partnerships grow and evolve, it is crucial to maintain a focus on equitable power dynamics and inclusive decision-making processes. Through robust governance structures and ongoing evaluation, stakeholders can ensure that these collaborations achieve sustainable and impactful outcomes. In embracing multi-stakeholder partnership models, the global community can forge a path towards innovative solutions and sustainable development, addressing the complex challenges that define our time with a spirit of cooperation and shared purpose.