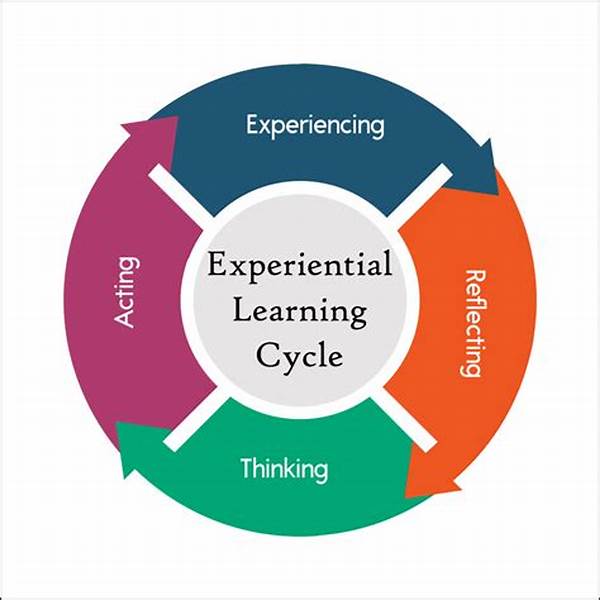
Experiential learning in career development is an innovative approach that emphasizes the significance of learning through direct experience. As individuals seek to navigate their professional paths, this method provides a bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical application. By integrating real-world experiences with academic understanding, experiential learning facilitates a deeper comprehension of complex career-related concepts, thereby enhancing professional growth and competency. This article delves into various aspects of experiential learning in career development, examining its implications, benefits, and applications.
Read Now : Unlocking Potential In Young Creatives
The Significance of Experiential Learning in Career Development
Experiential learning in career development plays a pivotal role in equipping individuals with the practical skills and knowledge necessary to excel in their chosen fields. This approach fosters an environment where learners are encouraged to engage actively with their tasks, enabling them to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. As they navigate real-world challenges, individuals gain insights into the dynamics of their industries, which helps them to adapt and innovate effectively. Experiential learning also encourages collaboration and communication, as individuals often work in teams to tackle projects, thus honing their interpersonal skills. Moreover, by reflecting on their experiences, learners develop self-awareness and a better understanding of their strengths and weaknesses, which are essential for personal and professional growth. In summary, experiential learning in career development not only enhances job-related competencies but also fosters a holistic development process that prepares individuals to face future challenges with confidence and competence.
Benefits of Experiential Learning in Career Development
1. Enhanced Skill Acquisition: Experiential learning in career development enables individuals to acquire and refine skills pertinent to their professions through direct application in real-world scenarios.
2. Increased Engagement: Learners tend to be more engaged when they actively participate in experiences that directly relate to their career goals.
3. Development of Critical Thinking: By confronting real-world challenges, individuals enhance their ability to think critically and solve problems effectively.
4. Improvement in Adaptability: Experiential learning encourages adaptability as individuals learn to navigate unforeseen challenges and changes in their professional environments.
5. Promotion of Lifelong Learning: The process instills a sense of lifelong learning, as individuals continuously seek new experiences to enhance their professional knowledge and capabilities.
Implementing Experiential Learning in Career Development Programs
Incorporating experiential learning in career development programs necessitates a structured approach to ensure learners gain maximum benefit. Programs should be designed to include diverse, hands-on experiences that are closely aligned with the learners’ career objectives. Such experiences might include internships, cooperative education, simulations, and project-based learning, each providing different perspectives and challenges. Instructors and mentors play a crucial role in guiding and supporting learners, offering feedback and encouraging reflective practice. This reflection is vital as it allows individuals to analyze their experiences, thereby deriving lessons and insights that contribute to personal and professional improvement. Furthermore, organizations should foster an environment that values learning and experimentation, encouraging employees to pursue diverse experiences and explore new facets of their careers. In crafting effective experiential learning in career development programs, it is imperative to maintain a balance between guided instruction and autonomous exploration, allowing learners to fully engage with and benefit from the learning process.
Challenges in Experiential Learning in Career Development
1. Resource Constraints: Implementing experiential learning can be resource-intensive, requiring time, financial investment, and trained facilitators.
2. Variable Learning Outcomes: The highly individualized nature of experiential learning means that outcomes can vary significantly between participants, making assessment challenging.
3. Integration with Curriculum: Ensuring that experiential learning aligns with educational standards and career objectives can be complex and time-consuming.
4. Risk Management: Real-world learning experiences can pose risks that need to be managed to ensure the safety and well-being of participants.
5. Scalability: Scaling experiential learning programs to accommodate large groups without losing the personalized learning experience can be difficult.
Read Now : Math Skill Enhancement With Adaptive Platforms
6. Access and Equity: Providing equal access to experiential learning opportunities for all students, regardless of their background or resources, remains a key challenge.
7. Stakeholder Buy-in: Obtaining buy-in from all stakeholders, including educators, employers, and students, is crucial but can be difficult.
8. Quality Control: Ensuring consistent and high-quality experiential learning experiences across different settings can be challenging.
9. Ethical Considerations: Experiental programs must be designed to prioritize ethical considerations and ensure that learners and community partners benefit equally.
10. Assessment Complexity: Creating effective assessment tools to measure the impact of experiential learning is complex and requires careful design.
11. Changing Nature of Work: The ever-evolving job market presents challenges to keeping experiential learning programs up-to-date and relevant.
12. Balancing Theory and Practice: Ensuring the right balance between theoretical knowledge and practical experience is essential for achieving holistic educational goals.
Future Directions in Experiential Learning in Career Development
The future of experiential learning in career development presents vast opportunities for enhancing educational and professional outcomes. As the workforce evolves, adaptive learning methodologies will be essential to equip individuals with the skills needed for emerging careers. Institutions are exploring virtual and augmented reality technologies to offer immersive experiential learning environments, providing learners with interactive simulations that closely mimic real-world scenarios. Additionally, global collaboration platforms are expanding, enabling learners to participate in international projects and gain diverse perspectives. These innovations promise to transform experiential learning in career development, making it more accessible and impactful. However, the implementation of these advancements will require thoughtful consideration to ensure they effectively contribute to the learners’ growth. It is crucial for educational institutions and organizations to maintain a focus on the practical application of theoretical knowledge, ensuring that curricula remain relevant and aligned with industry needs. As experiential learning continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play an integral role in shaping competent and innovative professionals capable of thriving in a complex and dynamic job market.
Conclusion on Experiential Learning in Career Development
In conclusion, experiential learning in career development stands as an integral component of modern education and professional training. Its focus on real-world application and reflective practice provides individuals with the practical skills and insights needed to navigate and excel in their chosen fields. By offering hands-on experiences, it bridges the gap between theory and practice, enabling learners to engage deeply with the content and develop a robust understanding of their professions. Furthermore, as the workforce continues to shift towards more dynamic and interdisciplinary approaches, the demand for such experiential learning opportunities is likely to increase. It is incumbent upon educators and employers alike to collaborate in designing and implementing effective experiential learning programs, ensuring they are inclusive, adaptive, and aligned with the evolving needs of the industry. Ultimately, embracing experiential learning in career development will foster a workforce that is not only skilled and knowledgeable but also adaptable and resilient, ready to meet the challenges and opportunities of the future.