Understanding Differentiated Math Instruction Strategies
Differentiated math instruction strategies are essential in addressing the diverse learning needs present in a modern classroom. These strategies are designed to tailor the teaching methods according to the students’ varying abilities, interests, and learning styles. By using differentiated math instruction strategies, educators can ensure that all students have access to meaningful learning experiences that are neither too easy nor overwhelmingly difficult. This approach begins with an understanding that each student has unique needs, and the teacher’s role is to facilitate an environment where all learners can thrive.
Read Now : Creative Acting Lessons Kids
Teachers employing differentiated math instruction strategies often use a flexible combination of content, process, and product modifications. Content differentiation involves varying the material being taught, process differentiation focuses on the methods used to teach, and product differentiation emphasizes the ways students demonstrate their learning. Such strategies support a more personalized learning pathway and promote greater student engagement and success in mathematics. Furthermore, differentiated math instruction strategies emphasize continuous assessment and adjustment based on students’ ongoing progress, which means teaching is both dynamic and responsive.
The implementation of differentiated math instruction strategies necessitates a commitment to knowing each student well. This includes understanding their academic history, interests, and preferred learning styles. Teachers are encouraged to gather data through formal assessments and informal observations to inform their instructional planning. As a result, these strategies help build a classroom culture that values diversity, encourages inclusivity, and fosters an environment where students feel confident in exploring complex mathematical concepts.
Key Components of Differentiated Math Instruction Strategies
1. Assessment-Driven Instruction: Differentiated math instruction strategies rely heavily on data collected from formative and summative assessments. This data helps educators tailor their approach to meet each student’s unique needs.
2. Flexible Grouping: These strategies encourage the use of varied grouping methods to cater to students’ learning preferences. Groups can be formed based on ability, interest, or learning style.
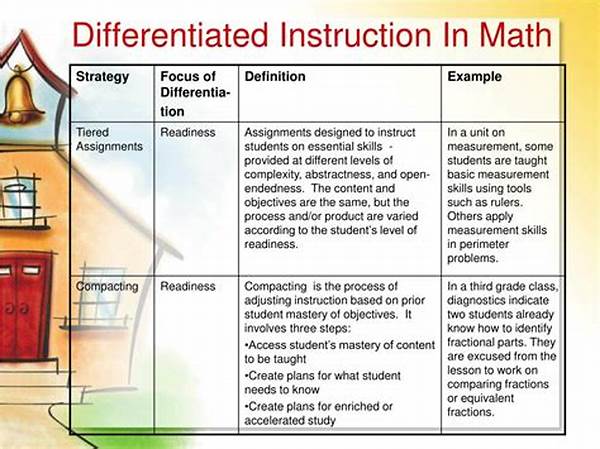
3. Tiered Assignments: Differentiated math instruction strategies incorporate tiered assignments that enable students to work at an appropriate level of complexity, ensuring they remain challenged and engaged.
4. Varied Instructional Methods: Techniques such as visual aids, hands-on activities, and technology integrations are part of differentiated math instruction strategies, appealing to multiple learning styles.
5. Ongoing Reflection and Adjustment: Teachers consistently reflect on the effectiveness of their differentiated math instruction strategies and make necessary adjustments to enhance student learning outcomes.
Benefits of Differentiated Math Instruction Strategies
Differentiated math instruction strategies offer a plethora of benefits for both students and educators. One primary advantage is the promotion of a more inclusive classroom environment where students are encouraged to share their ideas and approaches to problem-solving. This approach fosters a sense of community and collaboration among students, where each individual’s contribution is valued. Additionally, these strategies enable educators to address gaps in knowledge and support students in achieving their full potential.
Another significant benefit of differentiated math instruction strategies is the enhancement of student motivation and engagement. When students receive instruction that aligns with their interests and learning styles, they are more likely to take an active role in their education. This increased engagement leads to improved understanding and retention of mathematical concepts. Moreover, differentiated math instruction strategies help students develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills, as they are often encouraged to explore various methods of approaching complex problems.
Importantly, differentiated math instruction strategies also provide a framework for continuous professional development for educators. Teachers engaged in this approach develop a refined ability to assess student needs and craft lessons that effectively cater to a wide range of learners. As a result, educators are better equipped to foster an inclusive and dynamic learning environment that ultimately benefits the entire classroom community.
Implementing Differentiated Math Instruction Strategies: Twelve Key Steps
1. Assess students’ prior knowledge and skills.
2. Identify students’ interests and learning styles.
3. Develop a variety of learning activities.
4. Create a flexible classroom layout.
5. Use flexible grouping strategies.
Read Now : Math Skill Assessment And Adaptation
6. Design tiered assignments that cater to varying ability levels.
7. Integrate technology to support diverse learning needs.
8. Provide visual aids and manipulatives to enhance understanding.
9. Incorporate real-world applications into math problems.
10. Offer choice and autonomy in assignments.
11. Use continuous formative assessments to guide instruction.
12. Reflect on and adjust strategies based on student feedback and performance.
Challenges in Differentiated Math Instruction Strategies
Despite its numerous benefits, implementing differentiated math instruction strategies can present certain challenges. One of the significant obstacles is the time required for planning and preparation. Teachers need to design multiple lesson plans and materials to suit the diverse needs of their students. This demands a considerable investment of time and effort, which can be overwhelming, especially in classrooms with a large number of students. Effective time management and collaborative planning with peers can help mitigate these challenges.
Another challenge lies in the need for continuous professional development. Educators must stay informed about new strategies and resources that can enhance their differentiated math instruction practices. This continuous learning process can be intellectually demanding but is crucial for the successful implementation of differentiated math instruction strategies. School districts and educational institutions can support teachers by offering ongoing training and development opportunities.
Lastly, assessing student progress in a differentiated math classroom can be complex. Teachers must implement varied assessment methods to capture a comprehensive picture of each student’s understanding and needs. This complexity can be managed by utilizing a range of formative and summative assessment tools, allowing for a deeper insight into student progress. Ultimately, while challenging, these obstacles provide opportunities for growth and improvement in the classroom practice of differentiated math instruction strategies.
Conclusion on Differentiated Math Instruction Strategies
Differentiated math instruction strategies provide educators with an invaluable toolkit for fostering a supportive and effective learning environment. By acknowledging the individual needs and abilities of each student, these strategies promote a culture of inclusivity and engagement. Teachers are encouraged to adopt a comprehensive approach that includes assessment-driven instruction, tiered assignments, and flexible grouping, which collectively enhance students’ mathematical understanding and confidence.
While the implementation of differentiated math instruction strategies requires dedication, time, and professional development, the rewards are significant. Students benefit from a personalized learning experience that not only addresses their current needs but also prepares them for future mathematical challenges. As educators refine their approach and share best practices, differentiated math instruction strategies can significantly transform teaching and learning outcomes in mathematics. In conclusion, commitment to differentiated math instruction strategies allows for greater educational equity and success for all students.