The Importance of Experiential Learning for Career Readiness
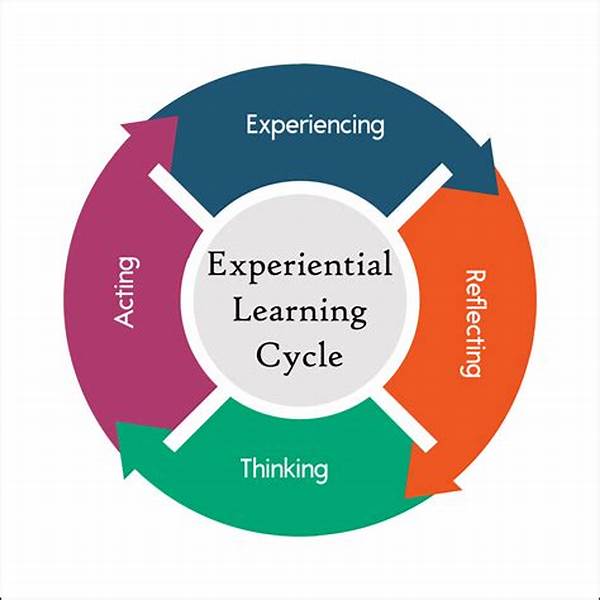
In recent years, experiential learning has increasingly been recognized as a crucial element in preparing individuals for successful careers. Experiential learning provides students and professionals with the opportunity to apply theoretical knowledge in practical settings, thereby enhancing their understanding and problem-solving skills. By engaging in real-world tasks and challenges, individuals develop competencies that are essential for career readiness. These competencies include critical thinking, collaboration, and effective communication, all of which are vital in today’s competitive job market. The concept of experiential learning emphasizes learning through reflection on doing, which not only deepens comprehension but also equips individuals with the agility to adapt in various professional environments.
Read Now : Real-world Applications In Learning
Moreover, experiential learning fosters a bridge between academic learning and career readiness. Traditional educational methods often focus on theory and memorization, which can leave graduates ill-prepared for the dynamic nature of modern workplaces. Experiential learning, on the other hand, integrates hands-on experiences with academic concepts, allowing learners to experience the practical applications of their studies firsthand. This integration results in a profound understanding of subject matter, making learners more versatile and capable when stepping into their careers. Consequently, experiential learning is instrumental in equipping future professionals with the tools necessary to thrive and excel in their chosen fields.
Additionally, employers increasingly value experiential learning as a critical component of career readiness. As industries evolve rapidly, employers seek candidates who possess not only academic knowledge but also practical skills and experiences relevant to their fields. Experiential learning enables individuals to develop such skills through internships, co-op programs, simulations, and project-based learning initiatives. These experiences allow prospective employees to showcase their ability to integrate theory with practical application—a quality that is highly sought after in any professional setting. Thus, experiential learning acts as a catalyst for career readiness, ensuring that individuals are not only knowledgeable but also prepared to meet the challenges and opportunities presented in their professional journeys.
Experiential Learning Models and Career Readiness
1. Internships: Internships are a quintessential component of experiential learning that significantly enhance career readiness. They provide students and entry-level professionals with real-world experience, exposing them to industry practices and workplace culture. Through internships, individuals can apply theoretical knowledge in practical settings, thereby gaining insights into their chosen fields. This firsthand experience not only refines their skills but also enhances their employability. By understanding industry dynamics and building professional networks, participants in internship programs prove themselves as ready candidates for future career opportunities and challenges.
2. Co-op Programs: Cooperative education (co-op) programs integrate classroom learning with paid work experience, fostering experiential learning and career readiness. These programs offer students alternating periods of academic study and practical employment, allowing them to gain a comprehensive understanding of their chosen professions. Through co-op programs, participants develop both technical and soft skills, making them well-prepared for the workforce. The structured exposure to industry practices and expectations enables students to transition smoothly from academic settings to professional environments, enhancing their readiness for successful careers.
3. Service Learning: Service learning combines community service with classroom instruction, emphasizing experiential learning and career readiness. This model allows students to engage in meaningful service projects that address real societal needs while applying academic concepts. Through service learning, individuals cultivate empathy, leadership, and teamwork skills, which are invaluable in any professional setting. Participating in such initiatives fosters a sense of social responsibility and provides students with a deeper understanding of their roles within communities. Consequently, this holistic approach enriches both personal growth and career preparedness.
4. Project-Based Learning: Project-based learning (PBL) is an experiential learning approach that significantly contributes to career readiness. In PBL, students tackle real-world problems and develop solutions through collaborative projects. This method fosters critical thinking, creativity, and effective communication skills, which are essential for professional success. By engaging in PBL, learners experience challenges and failures in a safe academic environment, preparing them to navigate complex issues in their careers confidently. The skills acquired through PBL empower students to be innovative and proactive contributors to the workforce.
5. Simulations and Role-Playing: Simulations and role-playing exercises are innovative tools in experiential learning that enhance career readiness. These activities provide participants with realistic scenarios where they can apply theoretical concepts and make decisions in a risk-free environment. Through simulations, individuals develop problem-solving abilities, decision-making skills, and emotional intelligence—competencies crucial for thriving in dynamic workplaces. Role-playing, in particular, allows individuals to understand different perspectives and practice interpersonal skills necessary for effective communication and collaboration, thereby preparing them for diverse professional settings.
Bridging the Gap Between Education and Career
In the contemporary landscape of education, bridging the gap between academic learning and career readiness is paramount. Experiential learning plays an integral role in achieving this objective, as it transforms theoretical knowledge into practical expertise. By immersing learners in real-world scenarios, experiential learning prepares them for the multifaceted challenges they will encounter in their careers. Schools and universities are increasingly incorporating experiential learning opportunities into their curriculums, ensuring that graduates are not only knowledgeable but also adaptable and proficient in real-life applications.
Furthermore, the implementation of experiential learning initiatives fosters stronger collaborations between educational institutions and industries. Through partnerships with businesses, organizations, and communities, students gain valuable exposure to professional environments before entering the workforce. These collaborations enable educational institutions to design curriculum that is aligned with industry needs, ultimately bridging the gap between education and career readiness. By prioritizing experiential learning, institutions are equipping students with the skills, experiences, and confidence required to transition seamlessly into successful career paths, while simultaneously fulfilling the demands of a rapidly evolving job market.
Key Components of Experiential Learning and Career Readiness
1. Authentic Experiences: Engaging in authentic experiences is central to experiential learning, enhancing career readiness by providing real-world contexts where learners can apply their knowledge.
2. Reflection: Reflection is a crucial step in experiential learning, allowing individuals to assess their experiences and derive meaningful insights that contribute to career readiness.
3. Skill Development: Experiential learning emphasizes the development of both technical and soft skills, ensuring that individuals are comprehensively prepared for successful careers.
4. Mentorship: Mentorship offers guidance and support in experiential learning, enriching the learning process and fostering career readiness by connecting individuals with industry professionals.
5. Interdisciplinary Approach: Employing an interdisciplinary approach in experiential learning broadens perspectives, equipping learners with diverse skills and knowledge for varied career opportunities.
Read Now : Systemic Governance And Management Practices
6. Industry Collaboration: Collaboration with industry partners in experiential learning provides learners with exposure to professional environments, boosting career readiness through practical experiences.
7. Innovation and Creativity: Experiential learning promotes innovation and creativity, enabling learners to apply novel solutions to real-world problems, which is indispensable for career readiness.
8. Flexibility and Adaptability: The dynamic nature of experiential learning cultivates flexibility and adaptability, essential attributes for navigating today’s ever-changing job landscape.
9. Cultural Competence: Experiential learning fosters cultural competence by exposing individuals to diverse perspectives, enhancing career readiness in globalized work settings.
10. Problem Solving: Developing problem-solving abilities is a cornerstone of experiential learning, preparing individuals to tackle complex challenges in their careers.
11. Teamwork and Collaboration: Experiential learning emphasizes teamwork and collaboration, vital skills for thriving in collaborative professional environments.
12. Lifelong Learning: Instilling a mindset of lifelong learning through experiential education ensures sustained career readiness in a world of continuous innovation and change.
Cultivating a Mindset for Continuous Growth
The significance of experiential learning in career readiness extends beyond immediate professional preparation, as it cultivates mindset attributes essential for lifelong growth. By engaging in experiential learning, individuals develop a proactive attitude towards learning, enabling them to adapt and thrive in an ever-evolving job market. This mindset fosters resilience, curiosity, and determination, all of which are important traits that contribute to sustained career development and success.
Experiential learning instills a sense of ownership over one’s learning journey, encouraging individuals to seek out learning opportunities beyond formal education. This independent pursuit of knowledge equips them to innovate, solve problems, and seize opportunities in their chosen careers. Through experiential learning, individuals cultivate an entrepreneurial spirit, empowering them to navigate uncertainty and continuously adapt to new challenges and advancements within their industries. Ultimately, the continuous growth mindset developed through experiential learning serves as an enduring asset, enabling individuals to remain competitive and resilient throughout their professional lives.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Experiential Learning
In summary, experiential learning plays an indispensable role in bridging the gap between education and career readiness. Through authentic, hands-on experiences, learners gain the skills, competencies, and confidence necessary for successful professional endeavors. As industries continue to evolve and demand multifaceted capabilities, experiential learning serves as a critical vehicle for equipping individuals with the agility and preparedness to excel in their careers.
The collaborative efforts between educators, institutions, and industry stakeholders in integrating experiential learning further reinforce its importance in fostering career readiness. By prioritizing experiential learning initiatives, educational systems are not only enhancing the employability of graduates but also contributing to more dynamic and innovative workforces. In a rapidly changing world, the value of experiential learning in shaping adaptable, skilled, and ready professionals cannot be overstated.