Importance of Multimedia Elements in Presentations
In the realm of professional and academic environments, the efficacy of multimedia elements in presentations cannot be overstated. These elements, encompassing audio, visual, and interactive components, serve to enhance the communicative value and engagement of a presentation. By integrating multimedia, presenters can transcend the limitations of text-based information, offering a dynamic and immersive experience for the audience. This engagement is crucial as it not only aids in capturing attention but also facilitates better retention of information. Studies show that individuals tend to remember data more effectively when it is presented through multiple mediums, making multimedia an indispensable tool in conveying complex ideas.
Read Now : Support For Early-stage Entrepreneurs
Moreover, multimedia elements in presentations cater to various learning styles within an audience. Visual learners benefit from slides that incorporate images and videos, while auditory learners find value in sound clips and narration. Additionally, interactive elements such as polls or quizzes can engage kinesthetic learners who thrive on active participation. This inclusive approach ensures that information is accessible to all, fostering an environment of inclusivity and understanding. Consequently, the strategic incorporation of multimedia not only broadens the reach of the presented content but also enriches the overall experience for all participants.
Lastly, the use of multimedia elements in presentations reflects a modern approach to information dissemination, aligning with current technological advances. In today’s digital age, audiences have become accustomed to receiving information through various digital platforms. Therefore, a presentation embedded with multimedia components resonates with contemporary expectations and meets the demand for multimedia literacy. This adaptation is imperative for maintaining relevance and ensuring effective communication in today’s rapidly evolving professional landscapes.
Types of Multimedia Elements in Presentations
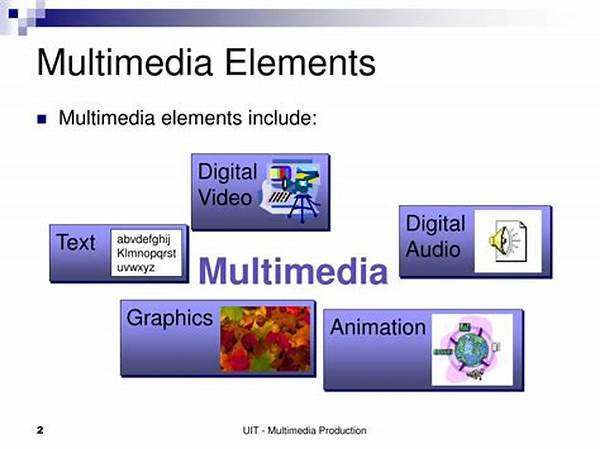
1. Visuals: The use of images, charts, and graphs in multimedia elements in presentations allows for a better understanding of statistical data and complex concepts. Visuals can simplify intricate information by depicting it in an easily digestible format.
2. Audio: Incorporating audio elements, such as voiceovers or background sound, can emphasize critical points and add an auditory dimension to multimedia elements in presentations, which enhances the audience’s engagement and understanding.
3. Video Clips: Video segments introduce dynamism, offering concrete examples or case studies within multimedia elements in presentations that can provide clarity and elicit emotional responses from the audience.
4. Animations: Animations bring static content to life, guiding viewers through transitions and processes in multimedia elements in presentations, thus aiding in comprehension and retention.
5. Interactive Features: Interactive elements like polls and quizzes transform passive viewing into active participation, engaging the audience in real-time interaction within multimedia elements in presentations, ensuring an immersive and memorable experience.
Benefits of Incorporating Multimedia Elements in Presentations
The integration of multimedia elements in presentations offers an array of profound benefits, essential for the successful delivery of content in contemporary settings. Foremost among these advantages is the enhanced ability to engage audiences. By utilizing a blend of audiovisual components, presenters can capture and maintain the attention of their audience more effectively than through text alone. This heightened engagement translates into improved comprehension, as multimedia stimulates the senses, making the presentation more accessible and enjoyable.
Furthermore, multimedia elements in presentations cater to diverse learning styles, which is pivotal in environments comprising varied audiences. By incorporating visual aids, auditory components, and interactive elements, presenters can reach visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners alike. This inclusive approach not only widens the scope of information delivery but also ensures that the message is comprehensively understood, thereby maximizing the efficiency of communication. Additionally, multimedia elements can break down complex ideas into simpler terms, using visual representations and sound to demystify challenging concepts.
Another notable advantage is the enhancement of message retention. When information is presented using multiple formats, it is more likely to resonate with the audience. This aspect is particularly critical in educational and professional scenarios where retaining information is paramount. Engaging multimedia elements make the content memorable, facilitating better recall. Moreover, multimedia lends a contemporary edge to presentations, aligning them with current technological expectations and enhancing the presenter’s credibility and the overall professionalism of the presentation.
Read Now : “virtual Classes With Accreditation”
Strategies for Effective Use of Multimedia Elements in Presentations
In the application of multimedia elements in presentations, it is vital to adhere to certain strategies to maximize their efficacy. First and foremost, content selection should be purposeful, ensuring that each element serves a clear objective, enhancing understanding rather than overwhelming the audience. Careful curation is essential to maintain focus and clarity throughout the presentation. Secondly, the use of multimedia should complement the overall narrative, seamlessly integrating with the verbal message to reinforce key points, thereby avoiding dissonance or confusion.
A balanced approach is also critical, whereby multimedia elements are used judiciously, avoiding excess that might detract from the core message. This entails striking a harmony between various media formats to provide a cohesive and engaging experience. Another strategy is ensuring technical compatibility and reliability; presenters must confirm that the chosen multimedia is adaptable to the technological environment in which the presentation will occur, minimizing technical difficulties that could distract or disengage the audience.
Furthermore, presenters should consider the demographic and cognitive preferences of their audience, tailoring multimedia elements in presentations to accommodate diverse needs and preferences. This ensures accessibility and inclusivity, fostering a more effective communication process. Finally, interactivity should be encouraged where possible, utilizing features such as polls or Q&A segments to foster active participation, creating a dynamic and responsive presentation environment, thereby enhancing audience engagement and retention.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Multimedia Elements in Presentations
Incorporating multimedia elements in presentations can pose several challenges, yet with strategic planning, these can be effectively mitigated. One significant challenge is the potential for technological malfunctions, which can disrupt the flow of a presentation. To counteract this, presenters should prepare by thoroughly testing all multimedia components prior to the presentation and having backup plans, such as alternative file formats or manual copies of key information, ready at hand. This preparation ensures a seamless presentation, regardless of any unforeseen technical issues.
Another challenge is the risk of cognitive overload, where the audience might become overwhelmed by an excess of multimedia content. To avoid this, presenters should strategically select elements that enhance rather than distract from the core message, maintaining a clear and simple narrative flow. This involves prioritizing essential information and using multimedia to clarify, rather than complicate, the content. In doing so, the cognitive load on the audience is managed, facilitating better comprehension and retention of information.
Finally, ensuring audience engagement in the presence of multimedia elements is essential. This can be challenging if the audience defaults to passive consumption. Incorporating interactive elements, such as live polls or discussions, encourages active participation, promoting engagement and attentiveness. Through mindful planning and audience-centered design, presenters can effectively overcome these challenges, making multimedia elements in presentations an asset, rather than a hindrance, in communication.
Conclusion
In summary, the implementation of multimedia elements in presentations is a powerful strategy for enhancing communication and engagement. These elements, when effectively leveraged, can transform a conventional presentation into an interactive and dynamic experience. By catering to diverse learning styles and incorporating various media, presenters can make their content more accessible and memorable. However, it is essential to navigate potential challenges such as technological malfunctions and cognitive overload carefully. With strategic planning and an audience-centered approach, the full potential of multimedia can be realized, ensuring presentations are both effective and impactful.