In the contemporary digital landscape, the significance of network security and access control cannot be overstated. The rapid evolution of technology and the increasing dependence on digital infrastructures necessitate robust measures to safeguard sensitive information and ensure uninterrupted operations. This article delves into the fundamental aspects of network security and access control, exploring their critical roles in protecting networks from unauthorized access and potential cyber threats. By implementing comprehensive security protocols, organizations can enhance their resilience against potential breaches and maintain the integrity of their technological environments.
Read Now : Unique Artistic Showcase Strategies
The Importance of Network Security
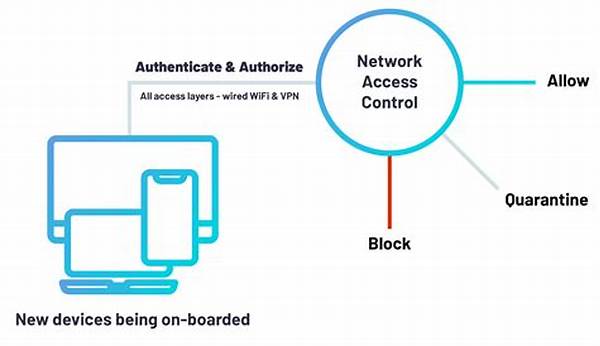
Network security constitutes a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity strategies. At its core, network security refers to the practices and tools designed to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data networks. This involves the deployment of various defenses, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption measures, to shield networks from unauthorized access and malicious activities. Equally crucial is access control, which governs who or what is permitted to access network resources. By meticulously managing network access through user authentication, authorization, and resource allocation, organizations can prevent unauthorized intrusions and data leaks. In essence, network security and access control are imperative for the continuous protection of digital assets, enabling a secure and resilient operational environment.
Network security encompasses a broad range of technologies and practices aimed at safeguarding data and maintaining an organization’s operational integrity. Access control serves as a crucial element within this framework, dictating policies that determine user permissions and resource accessibility. To achieve an optimal level of security, organizations are increasingly inclined towards multi-layered security architectures that combine network security and access control strategies. These architectures provide a fortified defense mechanism, enhancing the network’s ability to detect and neutralize potential threats. Ultimately, the synergy between network security and access control establishes a comprehensive defense posture, essential in today’s technology-driven business environments.
Strategies to Enhance Network Security
1. Deploying Advanced Firewalls: Firewalls serve as a barrier between internal networks and external threats, effectively monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security policies. By enhancing network security, organizations can ensure that only secure, authorized communications are allowed.
2. Implementing Intrusion Detection Systems: These systems play a vital role in identifying potential threats and unauthorized access attempts. By monitoring network activity, intrusion detection systems assist in the rapid identification and mitigation of risks, critical to maintaining effective network security and access control.
3. Strengthening Encryption Techniques: Encryption is essential for protecting sensitive data as it traverses networks. By converting data into secure formats, encryption ensures that even if intercepted, the information remains inaccessible without the appropriate decryption keys, thereby reinforcing network security.
4. Enforcing Strict Authentication Protocols: This involves implementing strong, multi-factor authentication measures to verify user identities, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized network access and ensuring that access control policies are robustly enforced.
5. Conducting Regular Security Audits: Regular audits are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities in network security and access control mechanisms. By systematically evaluating security infrastructures, organizations can proactively address potential weaknesses, bolstering their overall security posture.
Challenges and Future Perspectives
Prominent challenges in network security and access control include adapting to the dynamic nature of cyber threats and managing the complexities of network environments. As technology continues to evolve, cybercriminals advance their methods, necessitating continuous updates and advancements in security protocols. Furthermore, the increasing complexity of hybrid and multi-cloud environments presents additional challenges in implementing effective access control measures. By remaining vigilant and regularly updating security strategies, organizations can address these challenges and enhance their network protection efforts.
The future of network security and access control looks toward the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies. These advancements offer promising solutions for predicting and identifying potential threats by analyzing vast amounts of data in real-time. Through AI-driven systems, organizations can automate responses and improve their threat detection capabilities, leading to more resilient security frameworks. Nonetheless, the successful deployment of these technologies requires careful planning and ongoing evaluation to ensure their effectiveness in diverse network settings. Thus, the continued evolution of network security and access control practices remains a critical focus for organizations worldwide.
Evolving Threat Landscapes
The threat landscape for network security and access control is continuously evolving, with cybercriminals employing increasingly sophisticated tactics. Twelve critical components shape this evolving scenario, emphasizing the importance of vigilance and adaptation. First, advanced persistent threats pose a significant challenge, as they aim to infiltrate and remain undetected within a network for extended periods. Second, ransomware attacks leverage encryption to hold data hostage, demanding a heightened level of network security measures. Third, social engineering attacks exploit human psychology to breach access control systems.
Read Now : **automated Penetration Testing Software**
Fourth, insider threats arise when individuals with legitimate access misuse their privileges, emphasizing the need for stringent access control. Fifth, zero-day vulnerabilities highlight the urgency of proactive security measures, as they are unknown until exploited. Sixth, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks disrupt network availability, necessitating robust security protocols. Seventh, phishing attacks, disguised as legitimate communications, continue to threaten network integrity. Eighth, the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices introduces new vectors for network security breaches.
Ninth, blockchain technology presents both opportunities and challenges for access control. Tenth, supply chain attacks target security weaknesses within an organization’s external partners. Eleventh, AI-driven attacks leverage machine learning algorithms to bypass traditional security measures. Finally, twelfth, quantum computing poses future threats to encryption standards. Addressing these evolving threats requires organizations to prioritize network security and access control, ensuring the protection of critical assets and data.
The Role of Education and Training
Education and training play a pivotal role in fortifying network security and access control frameworks. Through comprehensive education, organizations can raise awareness of security practices among employees, equipping them with the knowledge to recognize and respond appropriately to potential threats. The emphasis should be placed on cultivating a culture of security consciousness, where every employee understands the importance of safeguarding network resources and adheres to established security protocols diligently.
Regular training sessions are essential for updating employees on the latest developments in network security and equipping them with practical skills to handle evolving cyber threats. By simulating real-world scenarios, training sessions offer an opportunity for employees to apply their knowledge and improve their decision-making in a controlled environment. Additionally, organizations should invest in specialized training for IT professionals, enabling them to deepen their expertise in network security and access control technologies.
Strategic partnerships with educational institutions and cybersecurity experts further enhance an organization’s capability to address emerging challenges and stay ahead of cyber threats. By fostering a learning-oriented environment, organizations ensure that their workforce is equipped with the skills necessary to support robust network security and access control practices, ultimately safeguarding the organization’s digital assets and maintaining operational integrity.
Summary of Network Security and Access Control
In summary, network security and access control are essential components in protecting organizations from the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. By implementing strategies such as deploying advanced firewalls, leveraging intrusion detection systems, and enforcing strict authentication protocols, organizations can enhance their defenses and prevent unauthorized access to their networks. Moreover, addressing challenges like adapting to dynamic cyber threats and managing complex network environments is crucial for maintaining robust security.
Ultimately, the successful implementation of network security and access control hinges on a collective effort that involves educating and training employees, staying informed about technological advancements, and regularly auditing security structures to identify vulnerabilities. By fostering a security-conscious culture and adopting a multi-layered security architecture, organizations can ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of their data, empowering them to navigate the digital landscape with confidence and resilience.